See latest deals:
In our increasingly digital world, we are often doing more and more work in front of our computer screens.
A poll by the Kaiser Family Foundation, Harvard’s Kennedy School of Government and National Public Radio shows that over two-thirds of American adults use a computer at work, and over 80 percent of them say that it is essential to their jobs. As work from home is also more and more popular, the time we spend in front of our screens has become a crucial part of our lives and thus, why it’s so important to pick the right screen for your type of work.
This is why many people, when thinking of buying a new monitor for their home computer, may get overwhelmed by the huge amount of options in the current market.
4K Resolution, 144hz, panel type, color accuracy, are all these just buzzwords made up by advertisers to sell more and more? We will be diving into what these are and how to figure out the best possible monitor for your particular use case.
Your Needs
As with many other things in life, when thinking about buying a monitor, the first question to ask is “What will I use this for?”
Depending on your specific needs, you might need a very specific type of monitor.
A very good gaming monitor, might be awesome for games, but can lack in features that are essential for video editing and production.
A 4K screen sounds nice, but will also increase the load of your graphics card while rendering image data.
There are many factors to consider, but the first thing is figure out what will you be using your monitor for, and we can go from there.
Screen Size and Resolution
The very first thing you may notice when shopping for a monitor is its size, and resolution.
Size simply refers to how physically big the screen is (usually in inches).
Resolution, means the amount of pixels a screen contains in its full surface. For example, a popular resolution is 1920 pixels wide, by 1080 pixels long
The amount of pixels and the size of your screen directly influences the clarity of the image you are seeing. The more pixels you have, the more visual data your eyes are receiving, so you will perceive a more clear image. This however, can be countered by having a monitor that is too big for the amount of pixels it contains. For example, imagine 2 monitors are both 1920×1080 pixels, but one of them is 24 inches, while the other is 27 inches.
The 24 inch monitor will have a higher PPI (pixels per inch), meaning that even though the 27 inches could be more attractive because of its bigger screen, it actually provides a worse image that is not as clear as the 24inch. A better resolution for a 27 inch monitor would be 2560×1440, another common format, while a 4k (3840 x 2160 pixels) monitor would normally look at its best, at 32 inches
Below, there is a small reference image of the differences between different resolutions.
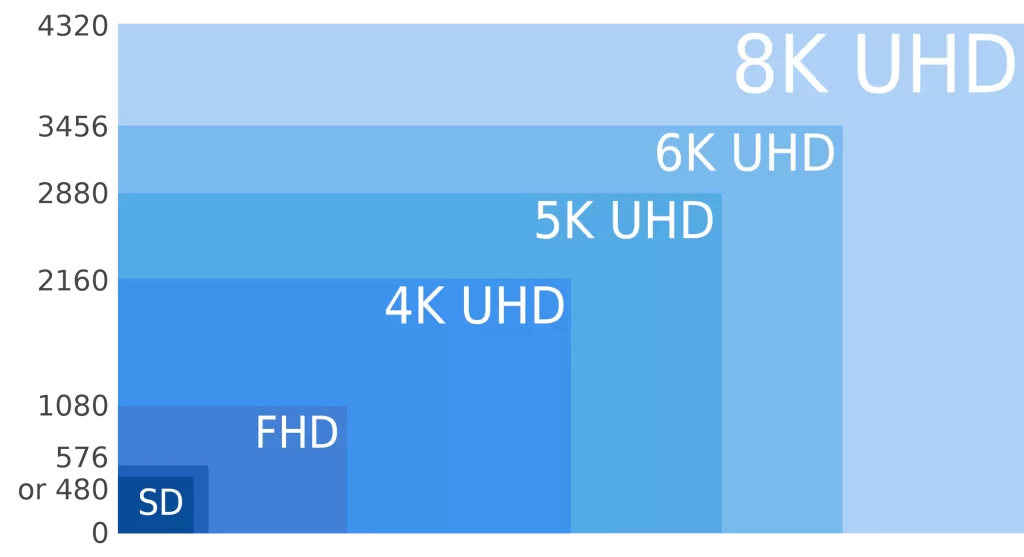
No single resolution size, out of the 3 most common ones, could be called bad. They would come down to personal preference, your use case, and your budget.
Panel Type
The Panel type refers to the manufacturing process of each monitor. Monitors of identical sizes and resolution, but with different panel types, can sometimes provide a very different viewing experience and you should do well to pick the one that suits you best.
Which do you need? TN, VA, or IPS? All modern monitors use TFT LCD (thin film transistor liquid crystal display) as their core technology. OLED is another option, and uses a completely different technology, organic light emitting diodes.
TFT LCDs have been around since the 1950s and have improved dramatically over time. There are three main types of panel: the oldest one, twisted nematic (TN), vertical alignment (VA) and in-plane switching (IPS).
IPS (In-Plane Switching):
Advantages: Excellent color accuracy and wide viewing angles. Ideal for tasks requiring precise color representation, such as graphic design and content creation. Also offers better viewing angles than TN and VA panels.
Disadvantages: Generally slower response times, making it less suitable for fast-paced gaming. Typically a bit more expensive.
Best Use Cases: Graphic design, video editing, content creation, general office work, and multimedia consumption.
TN (Twisted Nematic):
Advantages: Fast response times, making it suitable for gaming and fast-moving video. Typically more affordable than IPS and VA panels
Disadvantages: Limited viewing angles and less color accuracy compared to IPS panels. Colors can shift when viewed from different angles.
Best Use Cases: Competitive gaming, where speed is crucial, and budget-conscious consumers.
VA (Vertical Alignment):
Advantages: Good contrast and deeper blacks compared to IPS and TN panels. Better color accuracy and viewing angles compared to TN.
Disadvantages: Slower response times than TN panels, which may result in motion blur during fast gaming or video playback. Some models may suffer from “ghosting” effects.
Best Use Cases: Movie and multimedia consumption, general office tasks, and users who value deeper blacks and good color accuracy without the cost of an IPS panel.

This is a simplified version of this concept, but hopefully it will give you a good idea on what to expect for each one. It is really difficult to grasp the monitor differences when watching a youtube video on your own monitor, so if you really want to be sure, usually is best to head to any physical store where they have several types of monitors in display, and you can test out their differences.
As we’ve discussed, the choice of panel type depends on your specific needs and priorities. Generally, if color accuracy and wide viewing angles are crucial, go for an IPS panel. For competitive gaming, where speed matters most, TN panels are suitable. VA panels strike a balance between the two, making them a good choice for general use cases and multimedia consumption.
Refresh Rate and Response time
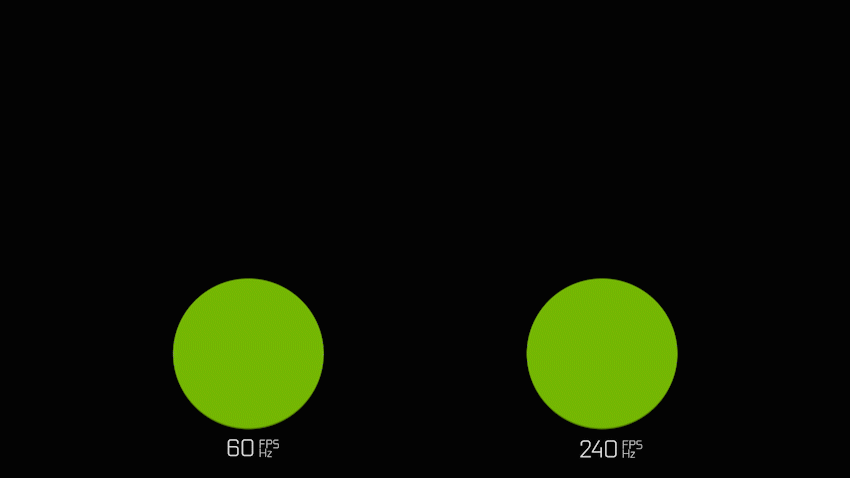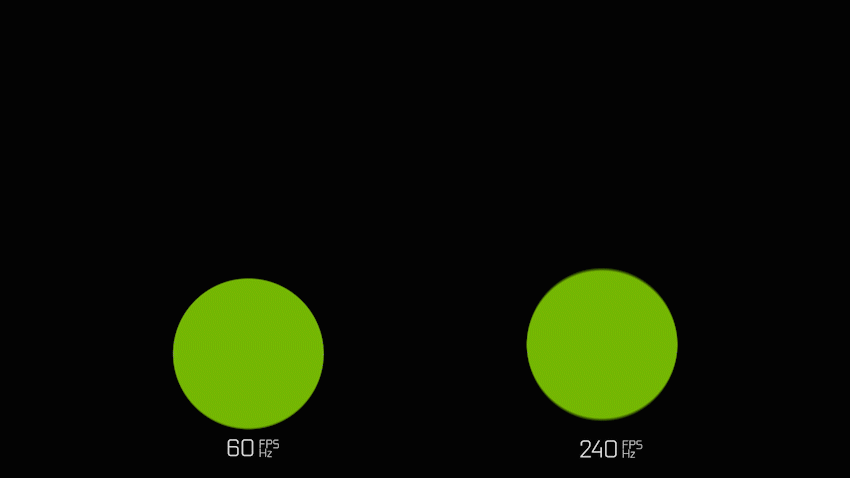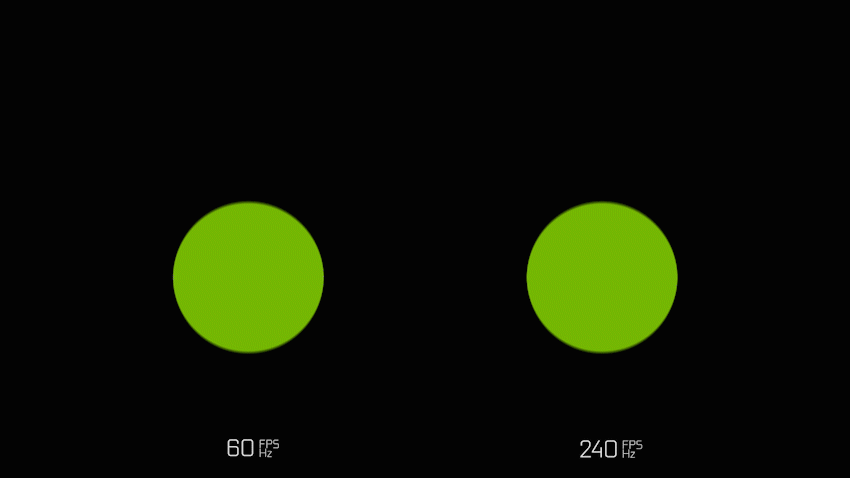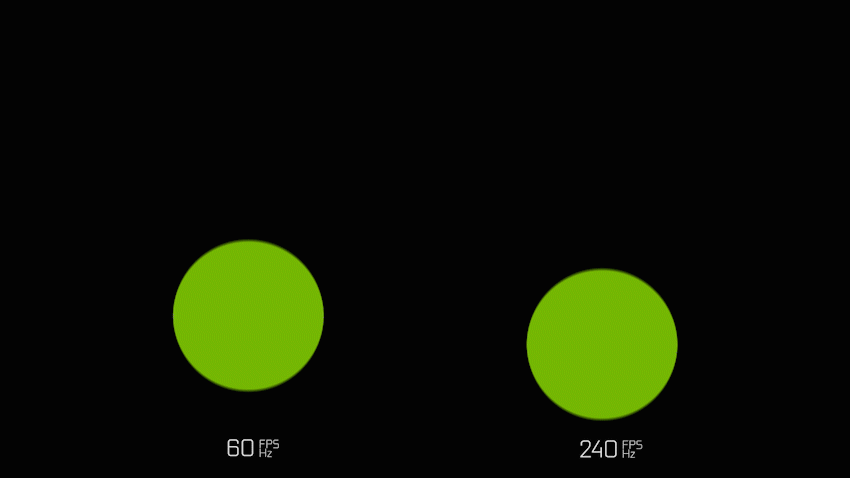
The refresh rate of your display refers to how many times per second the display is able to update the onscreen image. This is measured in Hertz (Hz). For example, if your display has a refresh rate of 144Hz, it is refreshing the image 144 times per second. The time between these updates is measured in milliseconds (ms).
If having a high FPS count is important for you, you’d want a high refresh rate monitor, starting at 144Hz or more. However the monitor can only display an image at the rate the system produces it, so it’s important that your CPU and GPU are capable of completing this process quickly.
Gamers will usually prefer a higher refresh rate of 144hz or more, due to the smoother gameplay experience it provides, reducing screen tearing and delivering a much more clear image when in rapid movement.
This improved smoothness can also be clearly noticed when scrolling a shopping website, social media, doing video editing, or 3D animation.
If you will be using your monitor mainly for writing documents, coding, modifying excel tables, watching movies and doing mostly stationary tasks where your monitor does not need to update very frequently, then you will be more than fine with a 60Hz monitor, as you will not really take full advantage of a high refresh rate.
What to purchase?
As in many other things, it depends on your usage.
Selecting the right monitor might appear to be a monumental task at times, considering the numerous types and combinations available. However, this variety is a positive aspect as it means you have the opportunity to determine your individual needs and preferences. Once you’ve identified what suits you best, you can choose from our recommended monitors or continue with your own research to find the perfect match for you.
By making a conscious and well-informed decision, you’ll ensure that you get the best possible visual experience, whether for gaming, video editing, office work, or any other task. The right monitor isn’t just a device; it’s a gateway to a more efficient and enjoyable digital life.














